Opcode |
Instruction |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0F E1 /r |
PSRAW mm, mm/m64 |
Shift words in mm right by amount specified in mm/m64 while shifting in sign bits. |
|
66 0F E1 /r |
PSRAW xmm1, xmm2/m128 |
Shift words in xmm1 right by amount specified in xmm2/m128 while shifting in sign bits. |
|
0F 71 /4 ib |
PSRAW mm, imm8 |
Shift words in mm right by imm8 while shifting in sign bits |
|
66 0F 71 /4 ib |
PSRAW xmm1, imm8 |
Shift words in xmm1 right by imm8 while shifting in sign bits |
|
0F E2 /r |
PSRAD mm, mm/m64 |
Shift doublewords in mm right by amount specified in mm/m64 while shifting in sign bits. |
|
66 0F E2 /r |
PSRAD xmm1, xmm2/m128 |
Shift doubleword in xmm1 right by amount specified in xmm2 /m128 while shifting in sign bits. |
|
0F 72 /4 ib |
PSRAD mm, imm8 |
Shift doublewords in mm right by imm8 while shifting in sign bits. |
|
66 0F 72 /4 ib |
PSRAD xmm1, imm8 |
Shift doublewords in xmm1 right by imm8 while shifting in sign bits. |
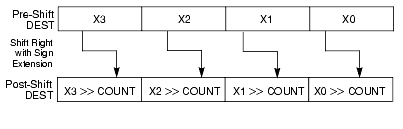
Shifts the bits in the individual data elements (words or doublewords) in the destination operand (first operand) to the right by the number of bits specified in the count operand (second operand). As the bits in the data elements are shifted right, the empty high-order bits are filled with the initial value of the sign bit of the data element. If the value specified by the count operand is greater than 15 (for words) or 31 (for doublewords), each destination data element is filled with the initial value of the sign bit of the element. (Figure 3-12 gives an example of shifting words in a 64-bit operand.)

The destination operand may be an MMX
The PSRAW instruction shifts each of the words in the destination operand to the right by the number of bits specified in the count operand, and the PSRAD instruction shifts each of the doublewords in the destination operand.
PSRAW instruction with 64-bit operand:
IF (COUNT > 15)
THEN COUNT 16;
FI;
DEST[15..0] SignExtend(DEST[15..0]
>> COUNT);
* repeat shift operation for 2nd and 3rd words *;
DEST[63..48] SignExtend(DEST[63..48]
>> COUNT);
PSRAD instruction with 64-bit operand:
IF (COUNT > 31)
THEN COUNT 32;
FI;
ELSE
DEST[31..0] SignExtend(DEST[31..0]
>> COUNT);
DEST[63..32] SignExtend(DEST[63..32]
>> COUNT);
PSRAW instruction with 128-bit operand:
IF (COUNT > 15)
THEN COUNT 16;
FI;
ELSE
DEST[15-0] SignExtend(DEST[15-0]
>> COUNT);
* repeat shift operation for 2nd through 7th words *;
DEST[127-112] SignExtend(DEST[127-112]
>> COUNT);
PSRAD instruction with 128-bit operand:
IF (COUNT > 31)
THEN COUNT 32;
FI;
ELSE
DEST[31-0] SignExtend(DEST[31-0]
>> COUNT);
* repeat shift operation for 2nd and 3rd doublewords *;
DEST[127-96] SignExtend(DEST[127-96]
>>COUNT);
PSRAW __m64 _mm_srai_pi16 (__m64 m, int count)
PSRAW __m64 _mm_sraw_pi16 (__m64 m, __m64 count)
PSRAD __m64 _mm_srai_pi32 (__m64 m, int count)
PSRAD __m64 _mm_sra_pi32 (__m64 m, __m64 count)
PSRAW __m128i _mm_srai_epi16(__m128i m, int count)
PSRAW __m128i _mm_sra_epi16(__m128i m, __m128i count))
PSRAD __m128i _mm_srai_epi32 (__m128i m, int count)
PSRAD __m128i _mm_sra_epi32 (__m128i m, __m128i count)
None.
#GP(0) - If a memory operand effective address is outside the CS, DS, ES, FS, or GS segment limit. (128-bit operations only.) If memory operand is not aligned on a 16-byte boundary, regardless of segment.
#SS(0) - If a memory operand effective address is outside the SS segment limit.
#UD - If EM in CR0 is set. (128-bit operations only.) If OSFXSR in CR4 is 0. (128-bit operations only.) If CPUID feature flag SSE-2 is 0.
#NM - If TS in CR0 is set.
#MF (64-bit operations only.) - If there is a pending x87 FPU exception.
#PF(fault-code) - If a page fault occurs.
#AC(0) (64-bit operations only.) - If alignment checking is enabled and an unaligned memory reference is made while the current privilege level is 3.
#GP(0) (128-bit operations only.) - If memory operand is not aligned on a 16-byte boundary, regardless of segment. If any part of the operand lies outside of the effective address space from 0 to FFFFH.
#UD - If EM in CR0 is set. (128-bit operations only.) - If OSFXSR in CR4 is 0. (128-bit operations only.) If CPUID feature flag SSE-2 is 0.
#NM - If TS in CR0 is set.
#MF (64-bit operations only.) - If there is a pending x87 FPU exception.
Same exceptions as in Real Address Mode
#PF(fault-code) - For a page fault.
#AC(0) (64-bit operations only.) - If alignment checking is enabled and an unaligned memory reference is made.
None.
For details, see Volume 2A and Volume 2B of the Intel(R) 64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Software Developer's Manual. For the latest updates on the instruction set information, go to the web site.